Evolution of intel computer processors It had 2, 300 transistors.This generational and chronological list of Intel processors attempts to present. Evolved from the capability processor developed for the BiiN joint venture with.Intels long-range vision for the evolution of these three eduardo bezerra uml pdf. May 23, 2018 The 8086, also known as the iAPX 86, was Intel's first commercial 16-bit CPU and is considered to be the chip that launched the era of x86 processors. With 29,000 transistors built in a 3,000 nm.
Evolution of Intel Processor since 19th Century. Intel is the masterpiece in computer processor world. Intel Corporation founded on 18 July 1968. The most successful processors from Intel since 1993 are listed with rare unseen pictures. I do collected interesting unknown information about each processor. 24: Processor Case Study 2CMOS VLSI DesignCMOS VLSI Design 4th Ed. Outline Evolution of Intel Microprocessors – Scaling from 4004 to Core i7 – Courtesy of Intel Museum. Sep 02, 2020 The Intel 4004 used MOS (metal–oxide–semiconductor) transistors. What has been the transistor types used in Intel processors onwards from the 4004 to 8085 to the x86 family of instruction set.
A microprocessor (sometimes abbreviated µP) is a digital electronic component with transistors on a single semiconductor integrated circuit (IC). One or more microprocessors typically serve as a central processing unit (CPU) in a computer system or handheld device.
Microprocessors made possible the advent of the microcomputer. Before this, electronic CPUs were typically made from bulky discrete switching devices (and later small-scale integrated circuits) containing the equivalent of only a few transistors.
By integrating the processor onto one or a very few large-scale integrated circuit packages (containing the equivalent of thousands or millions of discrete transistors), the cost of processor power was greatly reduced. Since the advent of the IC in the mid-1970s, the microprocessor has become the most prevalent implementation of the CPU, nearly completely replacing all other forms.
Various microprocessors |
The evolution of microprocessors has been known to follow Moore's Law when it comes to steadily increasing performance over the years. This law suggests that the complexity of an integrated circuit, with respect to minimum component cost, doubles every 24 months. This dictum has generally proven true since the early 1970s.
From their humble beginnings as the drivers for calculators, the continued increase in power has led to the dominance of microprocessors over every other form of computer; every system from the largest mainframes to the smallest handheld computers now uses a microprocessor at its core.
Microprocessors have impacted every type of computer that we use in our daily lives, from students studying for their bachelor degree online the ability do so anywhere at any time, to being able to find your travel destination with a GPS.
Without the introduction of microprocessors the computers we now have in our homes and even the one on your adjustable desk in your office would be vastly inferior to what we are accustomed to today. Simple tasks such as browsing the web and using word processors would be a monumental task.

History of the Microprocessor
The first microprocessors
As with many advances in technology, the microprocessor was an idea whose time had come. Three projects arguably delivered a complete microprocessor at about the same time, Intel's 4004, Texas Instruments' TMS 1000, and Garrett AiResearch's Central Air Data Computer.
Intel is the masterpiece in computer processor world. Intel Corporation founded on 18 July 1968. The most successful processors from Intel since 1993 are listed with rare unseen pictures. I do collected interesting unknown information about each processor. Hope you enjoy this post.
Original Pentium Processors
Year of release: 1993
CPU speed: 66MHz, 75MHz, 90MHz, 100MH up to 200MHz.
Socket: 273 pin PGA (Pin Grid Array)
Manufacturing technology: 0.8µ
Remarks: In 1993 this is the first processor capable of executing 112 million commands per second. This made easy for computers to process real world data such as sound, speech and photo images.

Pentium Pro Processors
Year of release: 1995
CPU speed: 166MHz, 180MHz and 200MHz
Socket: 387 pin PGA (Pin Grid Array)
Manufacturing technology: 0.6µ
Remarks: Primarily used for servers
Pentium MMX Processor
Year of release: 1997
CPU speed: 233, 266, 300, 333, 450 MHz
Manufacturing technology: 0.35µ
Socket: 296/321 pin PGA processor package.
Remarks: Support Intel MMX technology.
Celeron (Pentium II based) Processor
Year of release: 1998
CPU speed: 266, 300 MHz
Manufacturing technology: 0.25µ
Socket: 242 pin slot 1 single edge processor package (SEPP)
Pentium III and Pentium III Xeon Processor
Year of release: 1999
CPU speed: 500, 533, 600, 733, 800 MHz
Manufacturing technology: 0.18µ
Socket: 242 pin slot 1 single edge contact cartridge 2 (SECC2)
Remarks: Improved version of PII processor. Supports Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE) instruction set. SSE is the extension to x86 architecture. Introduced low power consumption in idle state technology.
Pentium 4 Processor
Year of release: 2000
CPU speed: 1.5, 1.6, 1.8, 2.0, 2.4 GHz
Manufacturing technology: 0.18µ
Socket: PGA 478, PGA 423 (Pin Grid Array)
Remarks: Used in desktop and entry level workstation systems
Intel Xeon Processor
Year of release: 2001
CPU speed: 1.4, 1.5, 1.7 and up to 3.6 GHz
Manufacturing technology: 0.18µ
Socket: OLGA 603 (Organic Land Grid Array)
Remarks: Used in high performance servers & workstations. Named as “Xeon” (not “Pentium Xeon”).
Intel Pentium M Processor
Year of release: 2003
CPU speed: 1.7, 1.8, 2.0 and up to 2.26 GHz
Manufacturing technology: 0.09µ (90nm) uses Nano technology
Socket: Micro-FCPGA and Micro-FCBGA (Flip-chip Ball Grid Array)
Remarks: Intel Centrino technology used. Intel Pro/wireless and network connection are the components of Centrino technology. Centrino technology specifically designed for portable computer such as Laptop.
Micro-FCBGA
Micro-FCPGA
Intel Itanium 2 Processor (Single core)
Year of release: 2002
CPU speed: 1 GHz up to 1.6 GHz
Manufacturing technology: 0.13µ
Socket: PAC611 (Pin Array Cartridge)
Remarks: New instruction set. Architecture is based on Explicitly Parallel Instruction Computing (EPIC). Designed for high end enterprise-class servers.
Intel Pentium D processor
Year of release: 2005
CPU speed: 2.6 and up to 3.2 GHz
Manufacturing technology: 0.065µ (65nm)
Socket: LGA 775 (Land Grid Array) also known as “socket T”
Remarks: Dual core technology introduced. First desktop dual core processor. Each core runs at same speed.
Intel Core 2 Duo and Dual-core Xeon Processor
Year of release: 2006
CPU speed: 1.8 and up to 2.93 GHz
Manufacturing technology: 0.065µ (65nm)
Socket: LGA 775 (Land Grid Array) also known as “socket T”
Remarks: Desktop and server processors with dual cores. Hyper threading, Intel VT-x, multiple OS support, SSSE3 SIMD instructions and Intel TXT (Trusted Execution Technology).
Intel Itanium 2 Processor 9000 series (Dual core)
Year of release: 2006
CPU speed: 1.6 GHz
Manufacturing technology: 0.09µ (90nm)
Socket: FC-LGA6 (LGA1248)
Remarks: Itanium processor with two cores. Performance has been doubled compare to previous version.
Quad core Intel Processors
Year of release: 2006 (Quad core Intel Core 2 Extreme and Quad core Intel Xeon Processors)
Year of release: 2007 (Core 2 Quad processor)
CPU speed: 2.66 GHz up to 3.2 GHz
Manufacturing technology: 65nm and 45nm
Socket: LGA 775 (Land Grid Array)
Remarks: 64 bit microarchitecture. These quad core processors were delivered fifty percent higher performance compare to dual core processors. New SSE4 instruction set for improved video, imaging and 3D content.
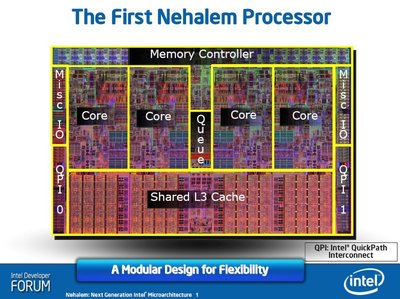
Intel Core i7 Processors
Year of release: 2008
CPU speed: 2.66GHz up to 3.20GHz (Turbo boost)
Manufacturing technology: 45nm
Socket: LGA1366
Remarks: 3-channel DDR3 RAM support. Integrated HD GPU. 4 physical cores. Front side bus replaced with QuickPath.
Intel Core i5 Processors
Year of release: 2009
CPU speed: 2.40GHz up to 3.60GHz (Hyper-Threading Turbo boost)
History Of Intel Processors Timeline
Manufacturing technology: 32nm
Evolution Of Intel Processors
Socket: LGA1156
Remarks: 2-channel DDR3 RAM support. Integrated HD GPU. 4 physical cores.
Intel Core i3 Processor
Year of release: Jan, 2010
CPU speed: 2.93GHz up to 3.33GHz
Evolution Of Intel Processors Family
Manufacturing technology: 32nm
Socket: LGA1156
Remarks: 2-channel DDR3 RAM support. Integrated HD GPU. 2 physical cores and 4 threads.
Intel Pentium Processors
Year of release: Jan, 2010
CPU speed: 2.8GHz and 2.93GHz
Cached
Manufacturing technology: 32nm
I9-10910
Socket: LGA1156
I9-10900K
Remarks: 2-channel DDR3 RAM support. Integrated HD GPU. 2 physical cores and 4 threads.